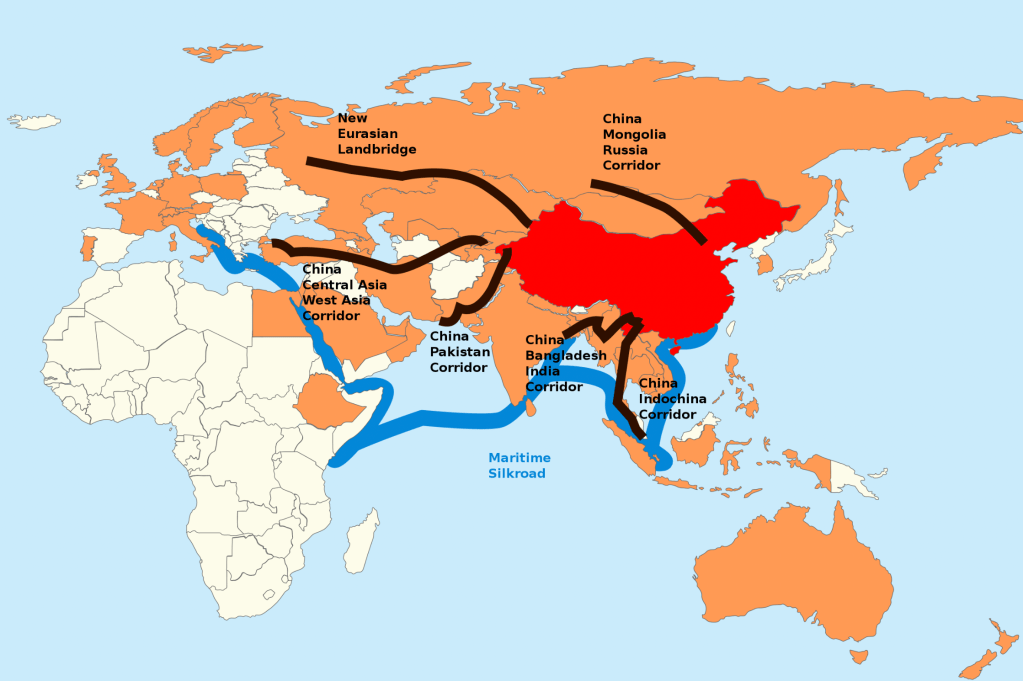
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), is a development strategy launched by the Chinese government in 2013. The strategy aims to boost economic development and connectivity between China and other countries in Asia, Europe, Africa, and beyond.
The “Belt” refers to the Silk Road Economic Belt, which is a network of overland transportation routes connecting China to Europe via Central Asia, the Middle East, and Russia. The “Road” refers to the Maritime Silk Road, which is a network of sea routes connecting China to Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and Africa.
The BRI Strategy involves the construction of new infrastructure, such as roads, railways, ports, and pipelines, as well as the development of new economic zones and trade corridors along the Belt and Road routes. China is investing heavily in these projects, with the aim of promoting economic development and trade in the regions along the routes.
The BRI strategy has been met with both enthusiasm and skepticism. Supporters argue that it could help promote economic growth and development in the regions along the Belt and Road routes, while critics argue that it could lead to unsustainable levels of debt for some countries and that it may be used by China to expand its geopolitical influence.
How has the BRI strategy impacted China’s geopolitical influence?
The BRI strategy has had a significant impact on China’s geopolitical influence. By investing in infrastructure projects in countries along the Belt and Road routes, China has been able to extend its economic and political influence beyond its borders.
One way that the BRI strategy has impacted China’s geopolitical influence is by strengthening its economic ties with other countries. By investing in infrastructure projects and promoting trade and investment along the Belt and Road routes, China has been able to deepen its economic relationships with countries in Asia, Europe, Africa, and beyond. This has helped to increase China’s influence in these regions and has given it greater leverage in international economic and political affairs.
The BRI strategy has also helped to promote China’s image as a global leader and champion of economic development. By investing in infrastructure projects in developing countries, China has positioned itself as a partner in their economic growth, which has helped to increase its soft power and influence in these regions.
However, the BRI strategy has also faced criticism from some countries and international organizations, who argue that it is being used by China to extend its geopolitical influence and promote its own interests. Some have raised concerns about the level of debt that some countries are taking on to finance these projects, and about the potential for China to use these projects to exert political influence over these countries.
So what is the drive for BRI by the Chinese, list some reasons
There are several drivers behind China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), also known as the One Belt, One Road (OBOR) strategy. Here are some of the main reasons:
- Foreign exchange reserves is one of the drivers behind the BRI. China has substantial foreign exchange reserves that are sitting in New York, and they do not want to bring them back to China due to inflation concerns. By investing in infrastructure projects in other countries, China can diversify its investments and potentially get better returns than US Treasuries. This can also help to mitigate the risks associated with relying too heavily on any one market, such as the US market.
- Geopolitical influence: The BRI also aims to extend China’s geopolitical influence beyond its borders. The BRI is one of the ways in which Xi’s vision for the Chinese Dream is being put into practice. By investing in infrastructure projects in other countries, China is seeking to promote economic growth and connectivity along the Belt and Road routes, which can help to advance its economic, social, and political goals. The BRI also provides an opportunity for China to extend its geopolitical influence and promote its vision for global governance.
- Resource security: China is also seeking to secure access to natural resources and raw materials by investing in infrastructure projects in countries that have these resources. By developing new trade routes and transportation networks, China hopes to improve its access to resources and reduce its dependence on traditional supply chains.
- Overcapacity: China has also been dealing with overcapacity in some industries, such as steel and construction. By investing in infrastructure projects in other countries, China hopes to alleviate some of this overcapacity by exporting its excess production to these new markets.
- Domestic stability: The BRI is also seen as a way to promote domestic stability in China by creating new job opportunities and promoting economic growth. By investing in infrastructure projects, China hopes to create new jobs and stimulate economic activity, which would in turn help to maintain social stability at home.
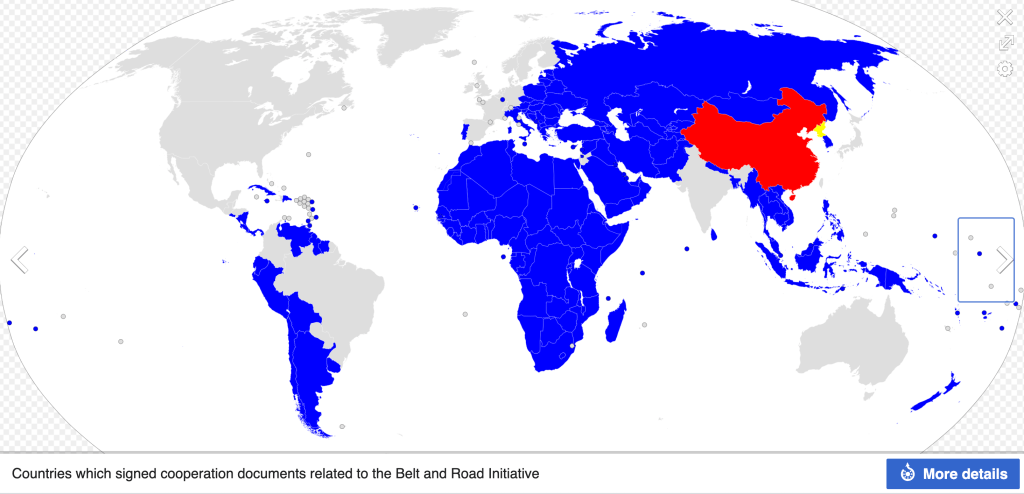
The BRI is driven by a combination of economic, geopolitical, and strategic considerations, and represents a major investment in China’s future growth and global influence. As of 2022, the total signs up for BRI has reached 149 countries, and Brazil could be the next country to sign BRI with China.

Leave a comment